In many countries around the world, pharmacy practice continues to embrace the use of herbalism and alternative medicines as an integral part of healthcare. These countries recognize the historical and cultural significance of herbal remedies, and how they can complement conventional medicine. This approach stands in contrast to some Western countries where the dominance of pharmaceuticals has marginalized herbalism and alternative medicines. A comparative analysis of healthcare statistics and costs reveals interesting insights into the benefits and challenges of incorporating herbalism into pharmacy practice.
Several countries, particularly in Asia, have a rich tradition of using herbal remedies in their healthcare systems. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), for example, utilizes a wide range of herbal medicines to promote health and treat various ailments. Similarly, Ayurveda, a traditional system of medicine in India, relies heavily on herbal remedies as well. These countries have continued to integrate herbalism into their pharmacy practice, recognizing its potential benefits in improving patient outcomes.
One key advantage of incorporating herbalism into pharmacy practice is the potential for cost savings. Herbal remedies are often less expensive than pharmaceuticals, which can help reduce healthcare costs. For example, a study by Xu et al. (2018) found that the average annual expenditure on herbal medicines in China was $29.84 per capita. In contrast, the average annual expenditure on pharmaceutical drugs in the United States amounted to $1,200 per capita (Keehan et al., 2020). In countries where access to healthcare and affordability are major concerns, the use of herbalism can be a cost-effective approach to healthcare provision.
Moreover, the use of herbalism in pharmacy practice in some countries has been associated with favorable healthcare statistics. Countries that have integrated herbal remedies into their healthcare systems have reported lower rates of certain chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes, compared to countries with a more pharmaceutical-centric approach. This suggests that herbalism, when used appropriately and in conjunction with conventional medicine, can contribute to positive health outcomes and disease prevention.
In contrast, the United States faces significant challenges in healthcare spending and the prevalence of preventable diseases. According to the Commonwealth Fund (2023), in 2021, the U.S. spent $11,072 per capita on healthcare, the highest among the countries analyzed in their study. This expenditure was significantly higher than countries such as South Korea, which spent $2,690 per capita. Despite the high spending, the U.S. lags behind other countries in terms of key health outcomes and preventative measures.
Let’s look at some graphs mapped out by the latest Commonwealth Fund (2021):
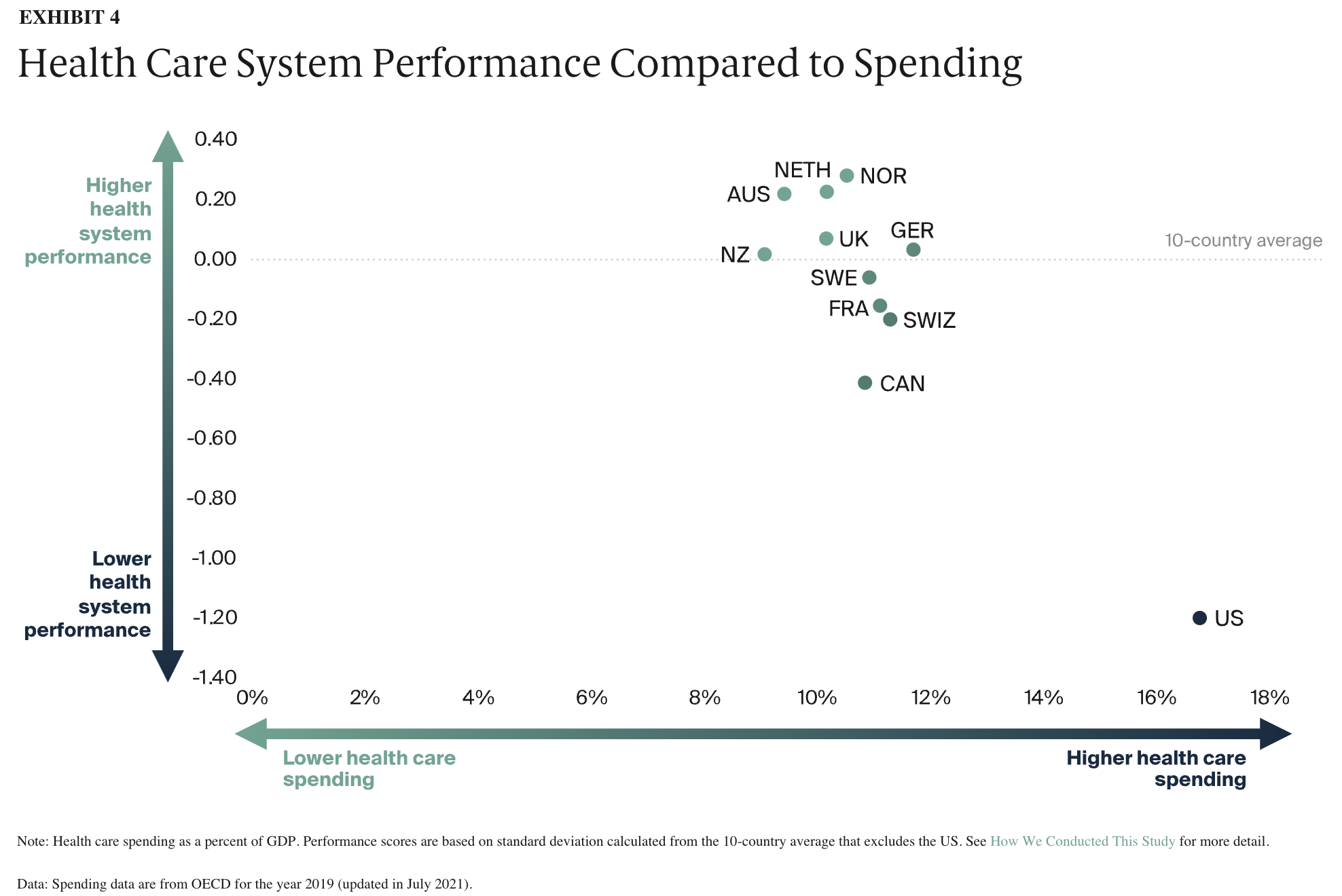
Despite the highest expenditures per capita, and spending the largest percentage of GDP (Gross Domestic Products), US lags far behind the other high-income “developed” countries according to analysis of the Commonwealth Fund reports in 2021. In addition, the morbidity and mortality efforts are significantly less impressive than other countries, as well as disparities between income and access between various groups. US ranks last for administrative and insurance complexities, which results in additional cost and access barriers to care. Residents of US and Canada are also more likely to use emergency room for non-emergency visits, and spend more time on paperwork (Source).
Risk factors for lifestyle diseases, including obesity rates, contribute to the burden of preventable diseases in the United States. The article from the Commonwealth Fund (2023) highlights that the U.S. has the highest obesity rates among the countries analyzed. Obesity is a major risk factor for chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers. The high prevalence of obesity contributes to the increased healthcare costs and disease burden in the United States.
Incorporating herbalism into pharmacy practice offers an alternative approach that can potentially address some of these challenges. Herbal remedies, when used in conjunction with conventional medicine, have the potential to contribute to disease prevention and promote patient-centered care. The cost-effectiveness of herbalism and its potential to improve healthcare outcomes make it an area worth exploring and considering in the context of pharmacy practice.
However, it is essential to address the challenges in incorporating herbalism into pharmacy practice, such as standardization, regulation, and evidence-based practices. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, regulatory bodies, and researchers are necessary to establish quality control measures and enhance the scientific understanding of herbal remedies.
Incorporating herbalism into pharmacy practice continues to be embraced in many countries around the world, with potential benefits in terms of cost savings, positive healthcare statistics, and patient-centered care. While there are challenges in terms of standardization and evidence-based practice, the integration of herbalism into pharmacy practice offers an alternative approach to healthcare that deserves further exploration and consideration. Comparative analysis of healthcare statistics and costs provides valuable insights into the potential advantages of incorporating herbalism into pharmacy practice, and offers opportunities for improving healthcare outcomes and addressing healthcare challenges.
References:
Commonwealth Fund. (2023). U.S. Health Care from a Global Perspective, 2022. Retrieved from https://www.commonwealthfund.org/publications/issue-briefs/2023/jan/us-health-care-global-perspective-2022
Eric C. Schneider et al., Mirror, Mirror 2021 — Reflecting Poorly: Health Care in the U.S. Compared to Other High-Income Countries (Commonwealth Fund, Aug. 2021). https://doi.org/10.26099/01DV-H208
Keehan, S. P., Cuckler, G. A., Poisal, J. A., et al. (2020). National Health Expenditure Projections, 2019–28: Expected Rebound in Prices Drives Rising Spending Growth. Health Affairs, 39(4), 704-714.
Xu, J., Yang, Y., Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Data Analysis Group, et al. (2018). The effectiveness and safety of complementary and alternative medicine for functional dyspepsia: A network meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018, 3408171.



